导读:本文由deepseek翻译,经观察者网编辑加工润色后发布。 【文/观察者网专栏作者 熊节、塞尔吉奥·阿马德乌】 人工智能领导权之争——中国与开源 为什么技术领导权如此重要?如何定义人工智能(AI)领域的技术领导权?人工智能是一项横跨多个领域的技术,其进步会对经济、社会和国家安全产生深远影响。技术领导权首先提供了一系列竞争优势,因为发明和创新赋予开发者其他人所不具备的收益和利益。其次,技术领导权是一个关键的地缘政治因素,因为它能够影响全球标准、规范和法规的制定。第三,技术领导权可以推动创新生态系统的形成,巩固长期发展。第四,领导权可以在国际威胁(包括军事威胁)的背景下增强安全性。第五,领导权能够引导技术发展,以实现社会、环境和政治目标。 从技术政治的角度来看,技术科学并非中立,它对权力关系和社会组织具有深远影响(Winner,2020)[1]。人工智能的领导权不仅仅是开发最先进的技术,还包括创建一个能够实现更广泛社会价值和目标的社会技术环境,确保创新遵循特定的目的。人工智能的发展轨迹可能会优先考虑提高经济系统的生产力,或者旨在寻找社会公正和环境可持续的解决方案。它可能寻求集中权力并加强国际不对称性,或者促进知识的传播和公平发展。它可能抑制人口和文化的创造力,或者确保技术多样性。它可能与权力的集中或分散密切相关。 目前,人工智能的领导权掌握在美国手中,主要由所谓的“科技巨头”主导。这些公司控制着开发现有人工智能(尤其是以深度学习为主导的人工智能)不可或缺的资源。 我们都知道,深度学习方法基于统计学和概率学,用于从大量数据中分类和提取模式。为了执行这些操作,人工智能开发者依赖于强大的计算能力。训练一个像ChatGPT这样先进的人工智能模型需要数百万美元,并且需要大量时间使用专用硬件进行处理,例如专为这些任务设计的芯片。这些芯片被称为“AI推理芯片”或“推理加速器”,它们能够在更短的时间内取得更好的结果。例如,谷歌的Tensor Processing Units(TPUs)专为推理和训练优化;神经处理单元(NPUs)或神经网络加速器常用于移动设备和边缘计算;图形处理单元(GPUs)则用于训练和推理。 目前,这些芯片对于图像识别、自然语言处理和其他实时人工智能任务至关重要。 美国政府长期以来一直采取限制尖端芯片获取的政策,主要目的是延缓中国和其他被视为对手国家的AI发展,目标是保持美国在AI领域的领导地位。随着唐纳德·特朗普于2025年1月就职,技术封锁政策进一步加剧。此外,美国总统宣布了一项5000亿美元的“星际之门”项目投资。特朗普的计划是与甲骨文、OpenAI和软银等公司合作,在美国开发物理和虚拟的AI基础设施,以“推动下一代AI的发展”[2]。英伟达、Arm和微软等公司是该项目的合作伙伴,该项目已在德克萨斯州开始实施,并将在未来四年内在美国各个地区建设“巨型数据中心”[3]。 以埃隆·马斯克为代表的美国科技精英认为,人工智能正在接近“奇点”——即人工通用智能(AGI)的出现。他们声称,AGI将完全超越并取代人类在所有智力领域的劳动,如果美国率先实现AGI,其技术霸权将不可撼动。然而,无论是ChatGPT还是DeepSeek,都没有显示出接近AGI的迹象。它们是处理自然语言的有用工具,并在特定领域展示了有限的推理能力,但没有证据表明它们——或任何已知的AI研究——正在接近AGI。  AGI比起一般的AI擅长以更像人类的方式去执行任务 开源的转折点 2024年5月,一家名为DeepSeek的中国小公司推出了其大型语言模型(LLM),该模型受到Llama的启发,Llama是一个禁止商业使用的受限研究协议下的模型。开源模型DeepSeek V2的突出之处在于其前所未有的成本效益。DeepSeek将推理成本降低至每百万个token仅1元人民币,约为Llama3 70B的七分之一,远低于GPT-4。 Token是语言模型用于处理和理解人类语言的基本文本单位,根据上下文和语言,token可以被视为单词、音节甚至单个字符的“块”。AI模型将文本转换为token,并以数字形式表示。这些数字随后由模型处理以生成响应或执行任务。因此,文本中的token数量直接影响成本和处理时间。token越多,推理越复杂且耗时。 与所有中国公司一样,DeepSeek也受到美国政府尖端芯片封锁的限制。这促使DeepSeek的领导者及其团队更加专注于研究和优化。梁文锋在2024年7月的一次采访中表示:“我们的出发点不是抓住机会发财,而是推进到技术前沿,以促进整个生态系统的发展。”[4] 这家中国公司试图引领AI发展的意图显而易见。为了实现这一目标,DeepSeek并没有局限于组织数据并在现有云平台上运行。团队努力在尖端芯片稀缺的情况下寻找解决方案。这需要改变架构、尝试新程序以及广泛的应用数学。 DeepSeek的年轻领导者梁文锋表示:“我们在创新方面缺乏的绝对不是资本,而是信心和如何组织高密度人才以实现有效创新的知识。”[5] 他继续说道:“创新并不完全由商业驱动,还需要好奇心和创造力。我们陷入了过去的惯性,但这也是暂时的。”[6] 梁文锋的理念是减少模仿,增加研究。他主张押注开源模型,不是为了使用它们,而是为了改进它们,并找到需要更少计算资源的路径。 开源是DeepSeek战略的核心,但对腾讯、百度和阿里巴巴等其他中国公司来说可能并非如此。然而,开源允许知识在全球范围内传播,从而以更快、更包容的速度产生新发现的可能性。梁文峰表示:“实际上,开源和论文的发表并没有损失。对于技术团队来说,被追随是一种巨大的成就感。事实上,开源更像是一种文化行为,而不是商业行为,因为给予实际上是一种额外的荣誉,这样做的公司也会更具有文化吸引力。”[7] 开源不是一种技术,而是一个基于知识共享的开发过程。通常,它鼓励组织愿意协作解决问题并通过更新维护解决方案的社区。像Mistral 7B(Mistral AI)和Falcon(技术创新研究所)这样的语言模型是开源的,并在Apache 2.0许可下发布;强化学习模型Stable-Baselines3也是开源的,采用MIT许可证。 那么,为什么DeepSeek的模型如此重要?因为它颠覆了全球AI领导权的竞争。如何做到的?通过大幅降低大型语言模型的计算成本。 开源对于知识传播至关重要,但并不能解决训练和运行模型所需的计算基础设施问题。DeepSeek展示了一个高性能且处理需求较低的开源模型。 DeepSeek-R1已经展示了比OpenAI的ChatGPT o1更强的推理能力,而其成本(包括训练和使用)显著降低。通过开源其模型,DeepSeek促进了大型语言模型的民主化——使技术基础设施欠发达的小公司、国家甚至个人能够基于DeepSeek训练自己的“主权AI”,而无需依赖科技巨头的产品或将数据交给这些公司。印度尼西亚和印度已经开始使用DeepSeek作为基础构建自己的AI基础设施[8]。在此之前,只有美国和中国有能力访问如此高水平的大型语言模型。 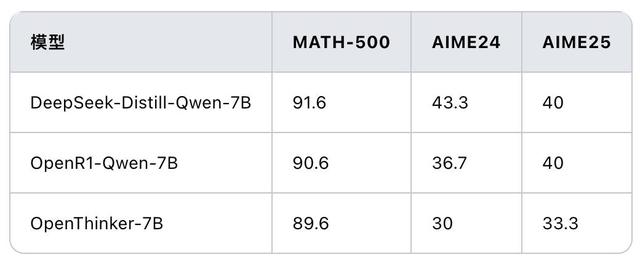 上表展示了在lighteval上OpenR1-Qwen-7B、DeepSeek-Distill-Qwen-7B和OpenThinker-7B的性能对比,可以看出在数学成绩上,OpenR1-Qwen-7B和DeepSeek-Distill-Qwen-7B差距不是非常明显。36氪 DEEPSEEK R1对强化学习的押注 “DeepSeek-R1-Zero选择了一条前所未有的路径,即‘纯’强化学习路径,完全放弃了预定义的思维链(CoT)模型和监督微调(SFT),仅依靠简单的奖励和惩罚信号来优化模型的行为。”[9] 在腾讯团队对DeepSeek R1模型的分析中,他们提出可能需要重新思考监督学习在AI发展中的作用。或许他们过于专注于让AI模仿人类的思维方式,而不是更多地押注于强化学习系统本身的解决问题能力[10]。在强化学习中,奖励和惩罚以数学方式表达在模型中。代理(可以是算法或系统)根据策略做出决策,该策略旨在最大化随时间累积的奖励。奖励是代理在环境给定状态下执行操作所获得的数值。 机器学习是人工智能的一个领域,它使计算机能够识别模式并根据数据做出决策,而无需明确编程[11]。机器学习依赖于从大量数据中提取模式并调整其参数以随时间提高预测能力的算法。这些算法可以分为三大类:监督学习(模型从标记数据中学习)、无监督学习(模型在没有预定义标签的情况下识别模式)和强化学习(模型通过试错学习,根据其行为获得奖励或惩罚)。深度学习是机器学习的一个子集,它使用具有多层的人工神经网络以分层和复杂的方式处理数据[12]。 由于这些创新,DeepSeek R1的训练成本大幅降低,仅为ChatGPT成本的1/10到1/20。当OpenAI的模型花费20美元时,DeepSeek仅用1美元就完成了相同的任务。2025年1月,DeepSeek模型的成本仅为每百万token 16元人民币,而ChatGPT的成本高达438元人民币——相差27倍![13] 这意味着组织可以以更低的成本使用DeepSeek的模型,同时实现更高的效率。 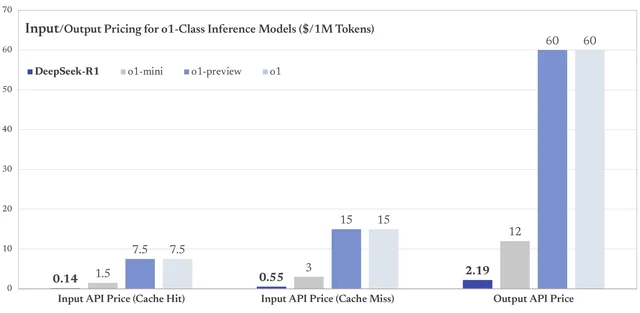 不同AI模型的Token输入/输出价格(美元/每百万Tokens),可以看到DeepSeek的价格远低于其他AI模型Reddit 计算能力与AI的地缘政治 英伟达和其他科技巨头股价的暴跌被许多人视为美国在AI领域领导地位的终结,这似乎并不准确。这家强大的GPU制造商的股价大幅下跌是由于在DeepSeek成功开发出成本仅为OpenAI 10%的大型语言模型的消息传出后,大量股票被抛售。这可能会改变AI的发展轨迹。对高处理能力芯片的依赖可能会发生变化。基于这种推理和恐惧,投机者趁机抛售了他们在英伟达和其他公司的股票。 然而,对尖端芯片的依赖并没有因为中国的创新而结束。小于2纳米的芯片代表了人工智能的关键进步,它们确保了更高的处理能力和更低的能耗。随着AI模型变得越来越复杂,需要数十亿甚至数万亿的参数,计算效率仍然是一个关键因素。更小的芯片允许更高的晶体管密度,提高计算速度和能源效率,降低运营成本和冷却需求。这一演进对于AI的大规模实施至关重要,从数据中心到移动设备,包括军事应用。 值得注意的是,纳米芯片扩展了设备中的嵌入式应用,并促进了它们在物联网、医疗保健、机器人(19.820, -0.77, -3.74%)和自动驾驶汽车中的使用。另一个承诺是,随着芯片变得更先进、体积更小,AI模型可以在本地运行,减少对云的依赖,并确保更快、更安全的响应。在地缘政治背景下,对更小芯片的竞争加剧了美国和中国等大国之间的技术争端,因为对这一技术的控制定义了数字经济和网络安全领域的竞争力。 美国通过技术主导、战略投资和供应链控制的结合,保持了在芯片和半导体开发和制造领域的领导地位。英伟达、英特尔、AMD和高通等美国公司引领着先进芯片的设计。美国政府通过补贴和激励措施(如《芯片与科学法案》[14])加强其地位,该法案拨款数十亿美元用于加强国内半导体生产,减少对亚洲的依赖。 除了技术优势外,美国还利用制裁和出口管制来限制战略竞争对手(如中国)获取关键技术。商务部对先进半导体制造设备(如ASML的机器和Cadence、Synopsys的芯片设计软件)的出口实施严格限制。这些限制使中国难以开发自己的先进芯片,并巩固了美国在该领域的地位。同时,华盛顿投资于战略联盟,如“芯片四方联盟”(与日本、韩国和中国台湾地区),确保其盟友遵循美国的指导方针,限制技术转让给被视为竞争对手的国家。这一综合战略使美国能够保持其在半导体行业的霸权,这对数字经济和国家安全至关重要。[15] 尽管美国正在尽一切努力限制中国获取先进芯片(7纳米以下)及其生产能力,但中国正在不断发展其独立制造这些高端芯片的能力。中芯国际(101.110, -3.21, -3.08%)(SMIC)已经展示了生产7纳米芯片的能力,并被认为很可能能够生产5纳米芯片[16]。上海微电子装备(SMEE)等公司正在积极开发极紫外(EUV)光刻技术,以取代ASML垄断的光刻机[17],这些光刻机已被限制向中国销售。 另一方面,在汽车和工业领域使用的成熟工艺芯片(技术并非最尖端但需求显著更高)方面,中国的芯片产业已经建立了大规模且完整的产业链。2024年,中国芯片出口总额超过1万亿元人民币(约合1390亿美元)[18]。可以预见,一旦中国公司在先进工艺上取得技术突破,其现有的供应链优势将显著降低高端芯片的价格。此外,芯片工艺受到物理极限的限制,无法无限改进。中国赶上美国只是时间问题。  美国前总统乔·拜登于2022年8月9日签署2022年《芯片法案》路透社 结论 “英伟达的领导地位不仅仅是一家公司努力的结果,而是整个西方技术社区和行业共同努力的结果。他们能够看到下一代技术趋势,并拥有路线图。中国的AI发展也需要这样的生态系统。许多国内芯片由于缺乏支持技术社区和二手信息而无法发展,因此中国需要站在技术前沿的人。”(梁文峰,2024)[19] DeepSeek的创始人梁文峰表示:“我们面临的问题从来不是资金,而是对尖端芯片的禁令。”[20] 即使数据集中化和对计算能力需求(需要越来越复杂的芯片)的趋势发生变化并失去动力,国际资本主义似乎也不会改变其根本的不对称性。毫无疑问,中国的技术科学发展使技术依赖美国的国家能够构建有利于其发展的战略。拥有主权、可控的世界级大型语言模型曾经是美国和中国以外的国家——尤其是全球南方国家——无法企及的。现在,DeepSeek已经民主化了这项技术,为全球南方国家在这一领域开辟了新的可能性。同时,这也为这些国家的政府提出了新的任务和挑战。 DeepSeek现象所指向的是开源对于加强国际协作链的重要性,这种协作链可以减少不平等和巨大的知识不对称。然而,开源并不能解决建设主权基础设施的问题,这些基础设施对于地方和国家发展至关重要。因此,寻求改善其技术经济地位的国家需要减少科技巨头的权力,控制AI的基本输入——尤其是来自其人口的数据——并投资于减少自动化系统在资本主义国家中产生的环境影响和劳动力不稳定的解决方案。押注于青年优质教育需要鼓励技术多样性,并将各民族的文化活力转化为技术表达。 【本文葡萄牙语版收录于即将在巴西出版的《人工智能,社会与阶级》(AI, Society and Class)一书】 注释: [1]Winner, L. (2020). The whale and the reactor: A search for limits in an age of high technology. University of Chicago Press. [2]https://startups.com.br/negocios/inteligencia-artificial/stargate-trump-anuncia-investimento-de-us-500-bi-em-projeto-de-ia/ [3] Idem. [4]https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/r9zZaEgqAa_lml_fOEZmjg [5]https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/r9zZaEgqAa_lml_fOEZmjg [6]Idem. [7]https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/r9zZaEgqAa_lml_fOEZmjg [8]https://www.lowyinstitute.org/the-interpreter/deepseek-diplomacy-disruption-dominance-data [9]郝博阳. (2025, 23 de janeiro). 一文读懂|DeepSeek新模型大揭秘,为何它能震动全球AI圈.腾讯科技. Link:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/cp4rQx09wygE9uHBadI7RA [10] Idem. [11] Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., & Courville, A. (2016). Deep Learning. MIT Press. [12] Idem. [13]https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/GG7l2P9ZveZjsHbS0AJ7Rg [14]https://www.congress.gov/bill/117th-congress/house-bill/4346 [15] Sutter, K. M., Sargent Jr, J. F., & Singh, M. (2023). Semiconductors and the CHIPS Act: The Global Context. Congressional Research Service (CRS) Reports and Issue Briefs. [16]https://www.dw.com/zh/%E7%BE%8E%E5%9B%BD%E5%88%B6%E8%A3%81%E4%B8%8B-%E5%8D%8E%E4%B8%BA%E7%AA%81%E5%9B%B4%E7%9A%84%E7%A7%98%E5%AF%86%E6%AD%A6%E5%99%A8%E6%98%AF%E4%BB%80%E4%B9%88/a-67530706 [17]https://www.dw.com/zh/%E7%94%B3%E8%AF%B7%E4%B8%93%E5%88%A9%E4%B8%AD%E5%9B%BD7%E7%BA%B3%E7%B1%B3%E8%8A%AF%E7%89%87%E5%85%89%E5%88%BB%E6%8A%80%E6%9C%AF%E5%8F%96%E5%BE%97%E7%AA%81%E7%A0%B4/a-70227975 [18] http://politics.people.com.cn/n1/2024/1205/c1001-40376144.html [19]https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/r9zZaEgqAa_lml_fOEZmjg [20] Idem. THE DISPUTE FOR LEADERSHIP IN ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE, CHINA, AND OPEN SOURCE Why is technological leadership important? How to define technological leadership in AI? Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a transversal technology, and its advancements have profound impacts on the economy, society, and national security. Technological leadership, first and foremost, provides a series of competitive advantages, as inventions and innovations grant their developers gains and benefits that others do not possess. Secondly, technological leadership is a critical geopolitical factor, as it allows for the influence of global standards, norms, and regulations. Thirdly, technological leadership can drive an innovation ecosystem that consolidates long-term development. Fourthly, leadership can enhance security in an international context of threats, including military ones. Fifthly, leadership enables the direction of technology to benefit social, environmental, and political objectives. From a technopolitical perspective, where technoscience is not neutral and has implications for power relations and social organization (Winner, 2020), leadership in AI is not merely about developing the most advanced technology but also about creating a sociotechnical environment that realizes broader social values and objectives, ensuring that innovation follows certain purposes. The trajectory of AI development may prioritize increasing productivity for the economic system or may aim to find socially just and environmentally sustainable solutions. It may seek to concentrate power and reinforce international asymmetries or contribute to the distribution of knowledge and equitable development. It may stifle the inventiveness of populations and cultures or ensure technodiversity. It may be tied to the concentration or distribution of power. Currently, AI leadership resides in the United States, under the direction of the so-called Big Techs. These companies control indispensable resources for the development of existing AI, particularly AI dominated by the deep learning approach. This approach is based on the use of statistics and probability for the classification and extraction of patterns from large amounts of data. To perform these operations, AI developers rely on significant computational power. Training an advanced AI model like OpenAI's GPT costs millions of dollars and requires many hours of processing with specialized hardware, such as specific chips designed for these tasks. These are called "AI inference chips" or "inference accelerators." They achieve better results in less time. For example, Google's Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) are optimized for inference and training. Neural Processing Units (NPUs) or Neural Network Accelerators, common in mobile devices and edge computing, are also used. Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) are utilized for both training and inference. Currently, these chips are essential for applications such as image recognition, natural language processing, and other real-time AI tasks. The U.S. government has, for some time, adopted a policy of restricting access to cutting-edge chips, primarily aimed at delaying AI development in China and other countries considered adversaries. The goal is to maintain U.S. leadership in AI. With Donald Trump's inauguration in January 2025, the policy of technological blockade was intensified. Additionally, the U.S. president announced a $500 billion investment in the Stargate project. Trump's plan is to develop physical and virtual AI infrastructures in the United States, in collaboration with companies like Oracle, OpenAI, and SoftBank, to "fuel the next generation of AI". Companies such as Nvidia, Arm, and Microsoft are partners in the project, which is beginning to be implemented in Texas and will, over the next four years, include "colossal data centers" across various regions of the United States. American tech elites, represented by figures like Elon Musk, believe that artificial intelligence is approaching the "singularity"—the emergence of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). They argue that AGI will completely surpass and replace human labor in all intellectual domains, and that if the United States is the first to achieve AGI, its technological hegemony will become unassailable. However, neither ChatGPT nor DeepSeek has shown any signs of approaching AGI. They are useful tools for processing natural language and demonstrate limited reasoning abilities within specific domains, but there is no evidence that they—or any known AI research—are nearing AGI. THE OPEN SOURCE TURNAROUND In May 2024, a small Chinese company called DeepSeek launched its Large Language Model (LLM) inspired by Llama, a model licensed under a restricted research agreement prohibiting commercial use. What stood out in the open-source model, DeepSeek V2, was its unprecedented cost-effectiveness. DeepSeek had reduced the cost of inference to just 1 yuan per million tokens, approximately one-seventh of Llama3 70B and significantly less than GPT-4. Tokens are basic units of text that language models use to process and understand human language. Depending on the context and language, tokens can be thought of as "chunks" of words, syllables, or even individual characters. AI models convert text into tokens, which are represented numerically. These numbers are then processed by the model to generate responses or perform tasks. Therefore, the number of tokens in a text directly affects the cost and processing time. The more tokens, the more complex and time-consuming the inference. DeepSeek, like all Chinese companies, was and is subject to the U.S. government's blockade on cutting-edge chips. This led DeepSeek's leader and his team to focus more on research and optimization. Liang Wenfeng, in an interview in July 2024, stated, "Our starting point is not to seize the opportunity to make a fortune but to advance to the forefront of technology to promote the development of the entire ecosystem." The Chinese company's attempt to lead AI development is evident. To achieve this, DeepSeek did not limit itself to organizing data and running on available clouds. The team worked hard to find solutions in the face of the scarcity of cutting-edge chips. This required altering architectures and experimenting with new procedures, as well as extensive applied mathematics. The young leader of DeepSeek, Liang Wenfeng, stated, "What we lack in terms of innovation is definitely not capital but confidence and knowledge on how to organize a high density of talent to achieve effective innovation." He continued, "Innovation is not entirely business-driven; it also requires curiosity and creativity. We are stuck in the inertia of the past, but this is also temporary." Liang Wenfeng's idea is to copy less and study more. To bet on open models not to use them but to improve them and find paths that require fewer computational resources. Open source is fundamental to DeepSeek's strategy but may not be for other Chinese companies like Tencent, Baidu, and Alibaba, among others. However, open source allows knowledge to be distributed globally, generating possibilities for new discoveries at a faster and more inclusive pace. Liang Wenfeng stated: "Actually, nothing is lost with open source and the publication of papers. For the technical team, being followed is a great sense of accomplishment. In fact, open source is more of a cultural behavior than a commercial one. Giving is actually an extra honor. A company that does this will also have cultural appeal." Open source is not a technology. It is a development process based on knowledge sharing. Generally, it encourages the organization of communities willing to collaboratively solve problems and maintain solutions by updating them. Language models like Mistral 7B (Mistral AI) and Falcon (Technology Innovation Institute) are open and licensed under Apache 2.0. The reinforcement learning model Stable-Baselines3 is also open with an MIT license. There are numerous other open models in the field of AI. So why did DeepSeek's model become so relevant? Because it disrupted the global race for AI leadership. How? By drastically reducing the computational costs of a large language model. Open source is fundamental for distributing knowledge but does not solve the problem of the computational infrastructure needed to train and run models. DeepSeek presented an open model with high performance and lower processing requirements. DeepSeek-R1 has already demonstrated stronger inference capabilities than OpenAI's ChatGPT o1, while its costs (including both training and usage) are significantly lower. By open-sourcing its model, DeepSeek has facilitated the democratization of large language models—enabling smaller companies, countries with less developed technological and digital infrastructure, and even individuals to train their own “sovereign AI” based on DeepSeek, without relying on Big Tech products or handing over their data to these companies. Indonesia and India have already begun building their own AI infrastructure using DeepSeek as a foundation. Prior to this, only the United States and China had the capability to access large language models at such a high level. DEEPSEEK R1'S BET ON REINFORCEMENT LEARNING "DeepSeek-R1 - Zero chose an unprecedented path, the path of 'pure' reinforcement learning, which completely abandoned the predefined Chain of Thought (CoT) model and supervised fine-tuning (SFT), relying solely on simple reward and punishment signals to optimize the model's behavior." In an analysis conducted by Tencent's team on the findings of DeepSeek's R1 model, they suggested that it might be necessary to rethink the role of supervised learning in AI development. Perhaps they were focused on making AI mimic how humans think rather than betting more on the native problem-solving capabilities of reinforcement learning systems. In reinforcement learning, rewards and punishments are mathematically expressed in the model. The agent (which can be an algorithm or a system) makes decisions based on a policy that seeks to maximize cumulative rewards over time. Rewards are numerical values that the agent receives for performing actions in a given state of the environment. Machine learning is a field of artificial intelligence that allows computers to identify patterns and make decisions based on data without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning relies on algorithms that extract patterns from large amounts of data and adjust their parameters to improve predictive capabilities over time. These algorithms can be divided into three main categories: supervised learning (when the model learns from labeled data), unsupervised learning (when the model identifies patterns without predefined labels), and reinforcement learning (when the model learns through trial and error, receiving rewards or penalties based on its actions). Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to process data in a hierarchical and sophisticated manner. Due to these innovations, the training cost of DeepSeek R1 was drastically reduced, representing only 1/10 to 1/20 of ChatGPT's cost. While OpenAI's model spent $20, DeepSeek performed the same activity with just $1. In January 2025, the DeepSeek model cost only 16 yuan per million tokens, while ChatGPT cost up to 438 yuan—a difference of 27 times! This means that organizations can use DeepSeek's model at a lower cost while achieving greater efficiency. COMPUTATIONAL POWER AND THE GEOPOLITICS OF AI The plummeting stock prices of Nvidia and other Big Techs were heralded by many as the end of U.S. leadership in AI. This does not seem to be accurate. The sharp decline in the value of the powerful GPU manufacturer was driven by the sudden sale of a massive volume of its shares following the news that DeepSeek had managed to develop a large language model at 10% of OpenAI's costs. This could change the course of AI. The growing dependence on high-processing chips might be shifting. Based on this reasoning and fear, speculators took the opportunity to sell their positions in Nvidia and other companies. The dependence on cutting-edge chips did not end with the innovations coming from China. Chips with less than 2 nanometers represent a crucial advancement for artificial intelligence. They ensure greater processing capacity with lower energy consumption. As AI models become more complex and require billions or trillions of parameters, computational efficiency remains a critical factor. Smaller chips allow for greater transistor density, improving calculation speed and energy efficiency, reducing operational costs, and the need for cooling. This evolution is fundamental for the large-scale implementation of AI, from data centers to mobile devices, including military applications. It is important to note that nanochips expand embedded applications in devices and favor their use in IoT, healthcare, robotics, and autonomous vehicles. Another promise is that with more advanced and smaller chips, AI models can be run locally, reducing dependence on the cloud and ensuring faster and more secure responses. In the geopolitical context, the race for smaller chips intensifies technological disputes between powers like the U.S. and China, as control over this technology defines competitiveness in the digital economy and cybersecurity. The United States maintains its leadership in the development and manufacturing of chips and semiconductors through a combination of technological dominance, strategic investments, and control of supply chains. American companies like NVIDIA, Intel, AMD, and Qualcomm lead the design of advanced chips. The U.S. government reinforces its position with subsidies and incentives, such as the CHIPS and Science Act, which allocates billions of dollars to strengthen domestic semiconductor production and reduce dependence on Asia. In addition to technological superiority, the U.S. uses sanctions and export controls to limit access to critical technologies by strategic rivals like China. The Department of Commerce imposes severe restrictions on the export of advanced semiconductor manufacturing equipment, such as ASML's machines and chip design software from Cadence and Synopsys. These restrictions make it difficult for China to develop its own advanced chips and reinforce the U.S. position in the sector. Simultaneously, Washington invests in strategic alliances, such as the "Chip 4 Alliance" (with Japan, South Korea, and Chinese Taiwan), ensuring that its allies follow U.S. guidelines to restrict technology transfer to countries considered competitors. This consolidated strategy allows the U.S. to maintain its hegemony in the semiconductor industry, essential for the digital economy and national security. While the United States is making every effort to restrict China’s access to advanced chips (below 7nm) and their production capabilities, China is continuously developing its ability to independently manufacture these high-end chips. Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation (SMIC) has already demonstrated the capability to produce 7nm chips and is believed to be likely capable of producing 5nm chips. Companies like Shanghai Micro Electronics Equipment (SMEE) are actively developing extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography technology to replace the lithography machines monopolized by ASML, which have been restricted from being sold to China. On the other hand, in the field of mature process chips used in automotive and industrial sectors—where the technology is not the most cutting-edge but demand is significantly higher—China’s chip industry has already established a large-scale and complete industrial chain. In 2024, China’s total chip exports exceeded 1 trillion RMB (approximately 139 billion USD) . It is foreseeable that once Chinese companies achieve technological breakthroughs in advanced processing, their existing supply chain advantages will significantly reduce the prices of high-end chips. Moreover, chip processing is constrained by physical limits and cannot be improved indefinitely. It is only a matter of time before China catches up with the United States. CONCLUSION "Nvidia's leadership is not just the result of one company's efforts but the combined efforts of the entire Western technology community and industry. They can see the next generation of technological trends and have a roadmap. AI development in China also requires this ecosystem. Many domestic chips cannot develop due to the lack of supporting technical communities and only second-hand information, so China needs someone at the forefront of technology." (Liang Wenfeng, 2024) The founder of DeepSeek, Liang Wenfeng, stated, "The problem we face has never been money but the ban on cutting-edge chips." Even if the trend of data concentration and the need for increasing computational power—which requires increasingly sophisticated chips—shifts and loses momentum, international capitalism does not seem to alter its fundamental asymmetries. Undoubtedly, the technoscientific development of China allows countries technologically dependent on the U.S. to structure strategies that benefit their development. Having sovereign, controllable, world-class large language models was once out of reach for countries outside the United States and China—especially those in the Global South. Now, DeepSeek has democratized this technology, opening up new possibilities for Global South countries in this field. At the same time, it has also presented new tasks and challenges for the governments of these nations. What the DeepSeek phenomenon points to is the importance of open source for strengthening international collaborative chains that can reduce inequalities and large knowledge asymmetries. However, open source does not solve the problem of building sovereign infrastructures essential for local and national development. Therefore, it falls to states seeking to improve their techno-economic position to reduce the power of Big Techs, control the fundamental inputs of AI—especially data from their populations—and invest in solutions that reduce the environmental impact and labor precarization that automated systems have generated in capitalist countries. Betting on quality education for youth requires encouraging technodiversity and converting the cultural vitality of peoples into technological expressions.   海量资讯、精准解读,尽在新浪财经APP
|